Which wars have been started by Russia?
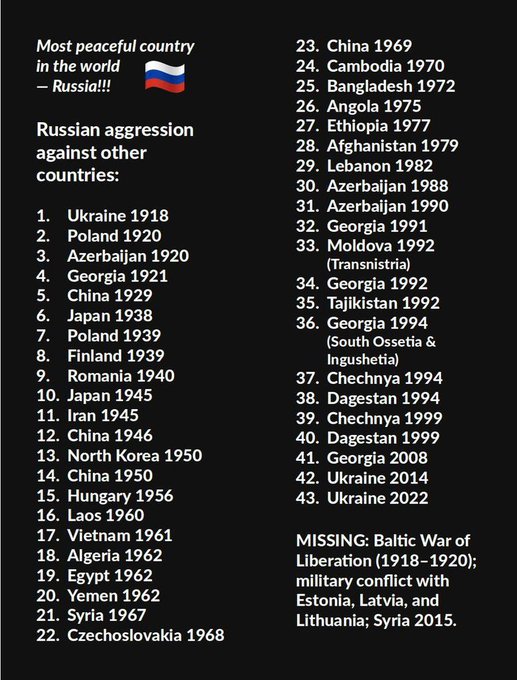
In Russian propaganda, a recurring theme is that they have never initiated an attack on any country. Instead, their propagandists and "historians" claim that other countries have always been the aggressors against their empire, starting from Karl XII, Napoleon, and Hitler. The reality is quite the opposite, and it may not be a historical coincidence that the world's largest country has also been the most aggressive throughout world history. The price paid by the Russian people has been poverty and war.
When Russians themselves read history, they often have an ethnocentric perspective. The Russian philosopher Ivan Ilyin (1883-1954), who is frequently quoted by Putin, wrote about Russian national identity and state power, advocating for political totalitarianism and a fascist state. Recurring themes in Russian war propaganda include portraying themselves as victims and being forced to attack Ukraine due to various circumstances, such as protecting their population from NATO expansion. What Putin is truly afraid of is the expansion of democracy and losing power himself. The following text summarizes some of the wars that Russia has most often initiated throughout history. We also include "democide," a term coined by Professor Rudolph Rummel, which can be described as "murder carried out by a national government," whether it involves political assassinations, mass killings, or genocides. In total, Sweden has been at war with Russia for approximately 100 years, and several of these wars were also initiated by Swedes, which has always been devastating for both countries.
Russia is a militaristic state that has ALWAYS been at war with other nations while simultaneously oppressing its own people.
Russia has been involved in a large number of wars over the past 800 years, both as an aggressor and a defender. Here are some examples of wars that have been started and initiated by Russia/Soviet Union:
Ukraine War 2022, ongoing: Russia's war in Ukraine, which Russia initiated on February 24, 2022, is characterized by terror against the civilian population. The Center for Civil Liberties has documented 27,137 war crimes during 2022.
Activities in African countries 2022, ongoing: Russian paramilitary groups, such as the Wagner Group, have been involved in activities in Mali and the Central African Republic since 2018. They now control several mineral resources and diamonds while supporting autocratic regimes. In Sudan, they have been involved in the theft of gold, which is used to fund the war in Ukraine. The Wagner Group has also been active in Mozambique, Libya, and Serbia. For several years, the Kremlin denied any connections to the Wagner Group. The group is led by Dmitry Utkin, a Nazi sympathizer, and takes its name from Hitler's favorite composer. It is supported by one of Putin's closest associates, Prigozhin. Read more about the Wagner Group.
involvement in Venezuela 2019: Russia supports the current government led by Nicolás Maduro, who is accused of executions, enforced disappearances, imprisonment of opposition members, trials of civilians in military courts, torture of prisoners, and suppression of protests. Together with China and Turkey, Russia has a strategic partnership in the region. The instability has resulted in refugee flows, epidemics, violence, corruption, drug trafficking, and other forms of lawlessness. Source
War in Syria 2015: Russia's support for dictator Bashar al-Assad. The Russian military representative, Leonid Ivashov, has claimed that part of the plan is to block oil pipelines to Europe. The Wagner Group has also been active in the conflict. According to The Syrian Network for Human Rightswhich has documented the number of casualties in Syria, Russian forces have killed 6,943 civilians, including 2,044 children and 977 women, and carried out 360 massacres. The Russians have conducted 1,243 attacks on civilian targets, including 223 schools, 207 medical facilities, and 60 markets.
The annexation of Crimea in 2014 In 2014, Russia annexed the Ukrainian peninsula of Crimea, which triggered the war between Russia and Ukraine. Initially, Putin vehemently denied Russian involvement. The soldiers involved lacked national insignia and were referred to as "little green men." Despite wearing Russian uniforms and using Russian equipment, Russian President Vladimir Putin claimed that they were not Russian but rather "local self-defense forces." However, overwhelming evidence pointed to direct Russian military intervention in Crimea. The annexation of Crimea by Russia remains a contentious issue internationally, with ongoing tensions between Russia and Ukraine.local self-defense unitsUntil 2017, a total of 9,800 people had been killed, leading to 1.4 million people fleeing conflict areas. On July 17 of the same year, Russian forces shot down Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, resulting in the deaths of 283 passengers and 15 crew members.
Air sabotage On the 17th of July of the same year, Russian forces shot down Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, resulting in the deaths of 283 passengers and 15 crew members.
The attack on Georgia in 2008. In 2008, Russia attacked the Georgian capital, Tbilisi, and other Georgian cities, resulting in a war between Russia and Georgia.
Hybrid warfare against the West since 2007. Russia conducts influence operations against democratic countries and supports extremist parties and anti-EU agendas in countries such as Hungary, Serbia, the United Kingdom, Italy, Brazil, Sweden, and the United States. Many agents operate as freelancers to enable plausible deniability of official involvement.
An interesting example is WikiLeaks' role in the U.S. presidential election and its connections to Russia and anti-Western propaganda. Russia Today and one of its founding propagandists, Margarita Simonyan, provided support to WikiLeaks. Julian Assange hosting his own TV show..
The Second Chechen War, 1999-2002: Initiated by Putin as a response to the region's bid for independence, Russia supported rebels in Chechnya. The European Court of Human Rights conducted an investigation that revealed numerous cases where the Russian government was found guilty of murder and torture. Source
Russia's wars, purges, military interventions, and genocides during the 20th century before Putin came to power.
Dagestan 1994 The First Chechen War broke out when Russian forces attempted to reclaim the breakaway republic of Chechnya in the North Caucasus over a two-year period from 1994 to 1996.
1991 In the same year Georgia declared independence from the Soviet Union, it led to a civil war between Georgia and Russians. In March, Russian bombs exploded in Lithuania, killing 14 Lithuanians as Moscow tried to suppress the country.
Tajikistan 1982 And a civil war between 1992-1997, where large parts of the country's infrastructure were destroyed. There were 20,000-60,000 casualties and 1.2 million internally displaced persons.
Georgia 1981

Azerbaijan 1988-1990: The conflict began in February 1988 when the Supreme Soviet (People's Assembly) of Nagorno-Karabakh, with a vote of 110-17, passed a resolution requesting to join its region to Armenia. January Massacre In 1990, the civilian population was suppressed.
Lebanon 1982: In the early 1980s, Syria was a strong regional power in Lebanon and had support from the Soviet Union. Syria also had a military presence in Lebanon, which was involved in the conflict in various ways. In 1982, Syria used its military force to try to regain control over the Palestinian refugee camps in Beirut, which were then under the control of the Palestinian guerrilla organization PLO. This led to a conflict with Israel, which was also involved in the conflict in Lebanon at that time.
The Soviet-Afghan War 1979-1989: In December 1979, the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan, leading to a protracted civil war in the country. Afghanistan had a Marxist government supported by the Soviet Union at the beginning of 1979. During the over nine years of Soviet occupation, it is estimated that around 1 million Afghans lost their lives, with the majority being civilians. Nearly 15,000 Soviet soldiers lost their lives, and a massive wave of millions of people became refugees. Source
Ethiopia 1977: In the early 1970s, Ethiopia had a military dictatorship supported by the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union also had a military presence in the country and provided weapons and other military equipment to Ethiopia.
Angola 1975: The conflict in Angola in 1975 was part of a long-standing civil war in the country that lasted from 1975 to 2002. The conflict involved several different groups and factions in the country, including various political parties and regional powers. At the beginning of 1975, Angola had a socialist government supported by the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union had a military presence in Angola and provided weapons and other military equipment to the government to defend itself against the guerrilla forces.
Cambodia 1970: In the early 1970s, Cambodia had a Marxist government supported by the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union had a military presence in Cambodia and provided weapons and other military equipment to the government to defend itself against the guerrilla forces. There are estimations that suggest several hundred thousand people lost their lives during the conflict.
China 1969:However, the two countries were involved in a conflict called the Zhenbao Islands Conflict, which took place between 1969 and 1979. The conflict resulted in a series of confrontations between Russia and China, including armed clashes between the two countries. There was no formal declaration of war, and the armed confrontations were relatively limited. Estimates suggest that several hundred people died.
The Soviet Union's military intervention in Czechoslovakia in 1968, known as the Prague Spring: The Prague Spring was a reform movement in Czechoslovakia that aimed to introduce democratic reforms. In 1968-1969, the Soviet Union intervened in Czechoslovakia and supported the pro-Soviet government, resulting in the country becoming part of the Warsaw Pact. There are estimations that suggest several thousand people lost their lives during this period.
Algeria 1962: The Algerian War of Independence took place between 1954 and 1962. The Soviet Union supported Algeria in the conflict by providing weapons and other military equipment to the country. It is difficult to determine the exact number of casualties in the conflict, but estimates suggest that several hundred thousand people died. The Algerian War of Independence led to Algeria's independence in 1962.
The Yemeni War of 1962-1963The Yemen War was a civil war in Yemen that took place between 1962 and 1970. The conflict involved various factions, including the royalists and republicans, vying for control of the country. The Soviet Union supported the Yemen Arab Republic, also known as North Yemen, during the war and provided military aid and equipment. They also supported Egypt's intervention in the conflict. The Yemen War resulted in the victory of the Yemen Arab Republic, which became an independent nation in 1970. The conflict caused significant casualties, with estimates suggesting that several hundred thousand people lost their lives.
The Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962A conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union, known as the Cuban Missile Crisis. It revolved around the Soviet Union's placement of nuclear weapons in Cuba, which prompted the United States to impose a blockade on the island and threaten military action if the missiles were not removed. The crisis reached its climax with the risk of escalating into a full-scale war between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Vietnam war 1955-1975 The Soviet Union and China supported North Vietnam during the Vietnam War. The Soviet Union provided weapons and other military equipment to North Vietnam throughout the conflict. The war resulted in the victory of North Vietnam, leading to the country's reunification and independence in 1975. The Vietnam War caused significant casualties, with estimates suggesting that several million people lost their lives.
China: There are reports of military clasheand confrontations along the border between the Soviet Union and China in the late 1950s.
The Laotian Civil War lasted from 1953 to 1975. The United States supported the Laotian government, while the Soviet Union supported the guerrilla groups during the Laotian Civil War. The Soviet Union provided weapons and other military equipment to the guerrilla groups throughout the conflict. The war resulted in significant casualties, with estimates suggesting that several hundred thousand people lost their lives. The Laotian Civil War concluded with the victory of the Laotian government, leading to the country's independence in 1975.
The Hungarian Revolution of 1956-1957The Hungarian Crisis revolved around a reform movement in Hungary seeking to introduce democratic reforms and establish a more decentralized society. The reform movement received support from a wide public in Hungary but faced opposition from the Hungarian government, backed by the Soviet Union. In October 1956, the Soviet Union and other Eastern European communist countries carried out a military intervention in Hungary to support the government and defend it against the reform movement.
Gulag death camps
Gulag The Gulag was a systematic organization of labor camps in the Soviet Union that existed from 1919 to 1956. These camps were used to detain and deport individuals who had committed political crimes or to forcibly labor individuals who had been convicted of non-political offenses. It is difficult to determine an exact number of people who were deported to the Gulag, but estimates suggest that it may have been as many as 15 million. Many of those deported died during their time in the camps due to harsh living conditions and strenuous labor.
1954 Post Stalin
A total of 6,872,000 killed in terror (250,000), death during deportations (8,000), and concentration camps (6,613,000).
Source: Professor RJ Rummel

Josef Stalin's reign of terror (1924-1954)
Professor RJ Rummel's book "Death by Government" has estimated that 62 million people were killed in democide inside and outside the Soviet Union during Stalin's regime. A common estimate of the death toll before the archives were opened was 20 million, and often the deaths due to famine are not included in the calculations. As a comparison, Rummel states that the number of deaths from Nazi Germany is 21 million
The largest system of mass murder belongs to the Soviet Union - the "Soviet Gulag state," as Rummel refers to it. "Old and young, healthy and sick, men and women, even infants and the weak, were cold-bloodedly killed." What makes this slaughter particularly mystifying is the fact that most of these victims were, as Rummel puts it, "guilty of... nothing."
Source and Wikipedia
The 1952 Catalina Affair where two Swedish signals intelligence aircraft (a DC-3 and a Catalina) were shot down by Soviet fighter jets in international waters.
North Korea 1950 The Korean War was a conflict that raged between 1950 and 1953 in South Korea and North Korea, involving several countries. Russia, or more specifically the Soviet Union, played a significant role in the conflict. The Soviet Union supported North Korea during the war, providing military and logistical assistance to the government in Pyongyang.
1946: A total of 15,613 killed in terror (1,376), death during deportations (1,557,000), and concentration camps (12,348,000).
Source: Professor Rudolph Rummel
World War II
Stalin and Hitler initiated the Second World War as allies, with their non-aggression pact, and they were friendly for 20 months after the war began. Germany attacked Poland several weeks before the Soviet Union. Poland lost 5 million people when they fought against both countries and lost 20% of its population.
Japan 1945The Soviet Union was involved in the war against Japan on its own borders in East Asia. The Soviet Union had a pact with Japan since 1939 but broke the pact in August 1945 and went to war against Japan. The Soviet Union attacked Japanese forces in Manchuria (northeastern China) and Korea, helping to weaken Japanese forces in the region. The Soviet Union also joined the Allied powers in the battles of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and participated in forcing Japan to surrender in August 1945.
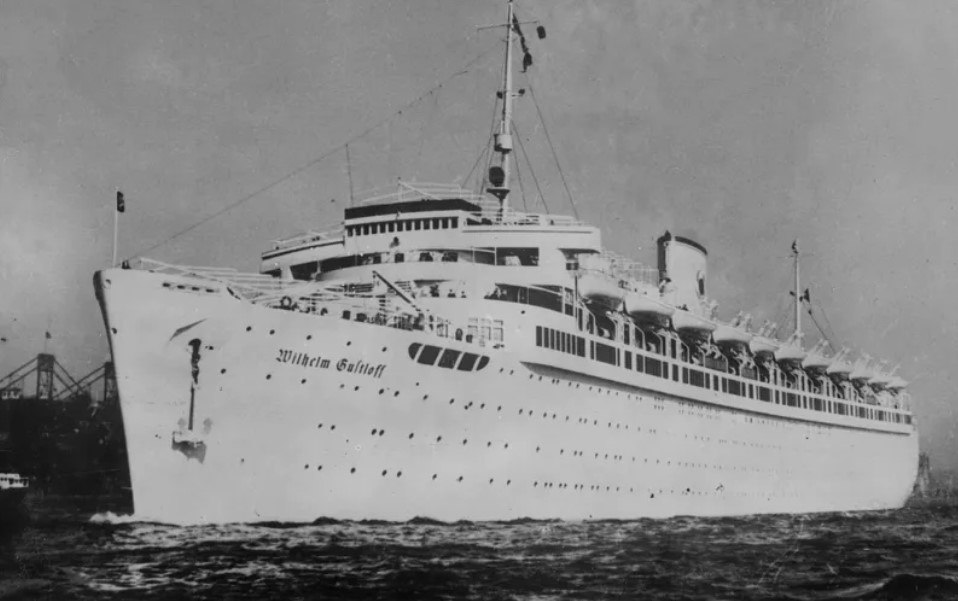

Baltic Sea 1945: The Russian submarine S-13 sank the German civilian passenger ship Wilhelm Gustloff in the Baltic Sea using torpedoes. On board were refugees from East Prussia, fleeing from the advancing Soviet forces. German Wikipedia reports death tolls ranging from 4,000 to 9,343. The disaster is considered the maritime tragedy with the highest number of fatalities in history. Source
Germany 1945: In late 1944 and early 1945, some six million Germans fled the advancing Red Army; most of the approximately six hundred thousand German refugees who died did so during this time. The Swedish The Gotland ferry Hansa was torpedoed on 24 November 1944 by Russian submarines and 84 people died from the passenger boat while two survived.
Many of the victims were people caught between the armies; some were massacred by Soviet soldiers or died in Soviet camps. The Russians carried out mass rapes in Germany. The estimated number of raped women is 2 million. The total number of German women who died as a result of Soviet mass rapes is estimated to be around 240,000, making it the largest mass rape in history. Source
The annexation of Königsberg in Germany took place during World War II, and the city was renamed Kaliningrad. In Kaliningrad, in 2013, Russia deployed Iskander missiles (9K720) with the capability of carrying nuclear warheads. In 2022, Russia has threatened several European states with nuclear weapons, including Sweden, Finland, Germany, France, Poland, the Baltic states, the United Kingdom, and specifically Washington in the United States.
1941: A total of 13,053,000 killed in terror (1,257,000), death during deportations (1,036,000), and concentration camps (10,761,000).
Source: Professor RJ Rummel
Romania 1941 The Soviet Union and Romania were involved in a conflict in 1941 when the Soviet Union attacked Romania and took over a large part of the country. After World War II, Romania was forced to become a Soviet satellite state. There are documented cases of mass executions, displacements, and oppression that occurred during this period. Romania was also one of the poorer countries in Eastern Europe during the communist era. The country had a low standard of living, low productivity, and high unemployment. Romania formally gained independence from the Soviet Union on December 22, 1989, following the wave of revolutions in Eastern Europe, and it has experienced increased economic prosperity since then.
Russia's attack on Poland during World War II During World War II, Russia invaded Poland alongside Germany, which had also attacked Poland. This war is known as the Second Partition of Poland. As part of this, the Russians entered into an alliance with the Nazi Germans in the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, where they divided Eastern Europe between themselves, and Russia acquired Eastern Poland, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Bessarabia.
Katyn massacre The massacres, which took place in Katyn and four other locations, are estimated to have resulted in approximately 22,000 deaths. These killings were orchestrated by the infamous NKVD chief, Lavrentiy Beria, who proposed the execution of all captured members of the Polish officer corps. This proposal was approved by the Politburo and Stalin. Additionally, tens of thousands of Poles and Balts died during or shortly after deportations to Kazakhstan and Siberia. Beria was notorious for his sexual abuses against young women but also engaged in serial killings of those who resisted. Stalin is said to have introduced him to at the Yalta Conference. Franklin D. Roosevelt with the words "it is our own Himmler”.
The Soviet Union carried out genocide and ethnic cleansing in the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania from 1939 to 1993. Source.

Winter war Russia's invasion and attack on Finland took place from 1939 to 1940. In 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Finland, leading to the Finnish Winter War. Russia's Continuation War with Finland took place from 1941 to 1944. At least 126,000 Soviet soldiers died during the Winter War, while Finland lost 25,000.
1939: Before World War II
1939: A total of 5,104,000 killed in terror (1,932,000), death during deportations (283,000), and Gulag concentration camps (2,889,000).
Source: Professor RJ Rummel
1936: The Great Terror: A total of 4,345,000 people were killed in terror (1,000,000), deaths during deportations (65,000), and Gulag concentration camps (3,280,000).
Source: Professor RJ Rummel

Holdomor
Ukraine 1932-1933 1929 launched Josef Stalin's collectivization of agriculture. where a total of 11,440,000 people died due to terror, concentration camps, and forced famine. It forced millions of peasants to abandon their farms and join collective farms. The result was a catastrophic famine known as the Holdomor due to the actions of the Soviet authorities. In Ukraine alone, approximately 3 million people died of famine, which is regarded by many as a genocide.
It is unclear whether the Kazakh famine of 1930-1932 was planned, but it is evident that over a million Kazakhs died of starvation. It is beyond reasonable doubt that Stalin intentionally starved Soviet Ukrainians to death during the winter of 1932-1933. Among Soviet documents from October to December 1932, there are a series of orders that testify to a criminal intent to kill.
1923 New Russian economic policy: A total of 2,200,000 people were killed. Source: Professor RJ Rummel.
The Soviet Union was founded on December 30, 1922.r after Lenin's victory in the war and the revolution
Georgia 1921Georgia became a Soviet republic in 1922 and remained part of the Soviet Union until 1991 when it declared independence again following the fall of the Soviet Union.
Azerbaijan 1921The Azerbaijani War of Independence took place from 1918 to 1920 when Azerbaijan sought independence from the Russian government. The war occurred in the context of the Russian Revolution and the Azerbaijani people established a provisional government that declared the country's independence.
Poland 1920 The Polish War of Independence occurred when the Soviet Union attempted to regain control over Poland. The war took place in what was then eastern Poland.
The War against the Baltic States 1918-1920 and the Baltic struggle for freedom, as the Baltic states sought independence from Russia. The Baltic states gained their independence during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1920, and these countries became independent nations.
The Gulag system started being used in 1919.
The red terror
Ukraine 1918, the Red Terror and the Civil War. Russia's war against Ukraine in 1918 was part of the Russian Civil War (1917-1922), which was fought between various factions in Russia after the Russian Revolution of 1917. The Bolsheviks viewed Ukraine as an opponent and sought to defend their power against the Ukrainian government, while Ukraine aimed for independence and freedom from Russian dominance.
The Civil War of 1917 and the Russian Revolution began in March in Petrograd. In total, 3,284,000 people were killed in terror (750,000), Gulag concentration camps (34,000), and forced famine (2,500,000).
Source: Professor RJ Rummel
In 1914, there was a tense situation between Scandinavia and Russia. In Bergen, Norway, Emperor Wilhelm's statue was unveiled, which had significant meaning for its time. Russia gets drawn into the First World War. The war exposes
the Russian state apparatus to severe strains and evolves towards increasing chaos.
The Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905: One military conflict that emerged from Japanese and Russian imperialist ambitions in East Asia, and Korea and ManchuriaThe war was initiated by Japan. Russia lost the war, and Japan gained territorial gains as a result of the peace settlement. Subsequently, a revolution broke out in Russia.
Wars initiated by Russia in the 19th century.
1899 A Russian committee led by Kuropatkin proposed a plan for the Russification of Finland and its assimilation into the Russian army, leading to a coup d'état in 1899. They stripped the Finnish Parliament of its legislative power, and the Tsar declared that Finland's state treasury would pay 10 million marks annually to Russia to avoid military service. Simultaneously, all railways in Finland were altered to align with Russian standards.
In 1877, Russia declared war against the Ottoman Empire. Russia declared war against the Ottoman Empire in 1877 in response to the Ottoman policy of closing the Suez Canal to Russian ships during the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-1878. Russia also declared war against the Ottoman Empire to defend its interests in Eastern Europe and to increase its power and influence in the region. Russia had long sought to expand its borders and gain control over territories that were previously under Ottoman rule, and the war against the Ottoman Empire was part of this strategy. After the war, the Treaty of Berlin was signed, granting Russia control over territories in Eastern Europe and increased trade rights in the Ottoman Empire.
In 1867, there was a tense situation between Tsar Alexander II of Russia and Scandinavia. However, no war broke out. When the Swedish government became aware of these plans, they shared the information with Berlin, and the Prussian General Schweinitz traveled to Norway. The Prussian ambassador in Petersburg confidentially expressed their concerns to the Russian Foreign Ministry and lodged a protest against Russia's stance towards Sweden and Norway.
The 19th February 1861 Serfdom was abolished in Russia by Tsar Alexander II. According to a Russian census from 1857, the country's population was 62 million, of which 23 million were serfs. Meanwhile, in the United States, there were 4 million enslaved individuals at the same tim Source
During the Crimean War, which began in 1853 the Russian Tsar Nicholas I (reigned 1825-1855) ordered his armies to march into Moldavia and Wallachia (These two states were Ottoman principalities where Russia claimed to be a special protector of the Orthodox Church). Nicholas is known for his reactionary policies and harsh treatment of political opponents. He also implemented a series of restrictive laws that curtailed freedom of speech and censored the press.
Treaty of Kulja The Treaty of Kulja, signed on July 13, 1851, was an agreement between the Qing Dynasty of China and the Russian Empire. The treaty established the border between the two countries in Central Asia, specifically between Xinjiang in China and eastern Kazakhstan.
In 1840, Tsar Nicholas had reorganized his army and pursued the expansionist plans of his predecessor. In Norwegian Finnmark, Russian tourists conducted surveys to identify which ports did not freeze, which were the most advantageous for military purposes, and which routes led from Finnish territory to the sea. They attempted to negotiate for the coast of Varangerfjord in exchange for a mountainous region in Finland. As the negotiations did not progress, they blocked the Finnish border, preventing the Norwegian Sami people's reindeer herds from accessing the area. In response, the Norwegian government excluded Russian fishermen from the Norwegian Arctic fisheries. War was on the brink, but then the Crimean War broke out.
Russia's invasion of Poland in 1831: In 1831, Russia invaded Poland and initiated a series of conflicts known as the November Uprising.
Russia's invasion of Turkey in 1828: In 1828, Russia invaded Turkey and initiated the First Russo-Turkish War.
Russia's invasion of Persia (Iran) in 1826. In 1826, Russia invaded Persia and initiated the Persian-Russian War.
The Napoleonic Wars and the Finnish War.
According to Putin's propaganda, it may sound as if Russia was attacked by all of Europe, which is far from the historical truth, as the maps were redrawn significantly during the Congress of Vienna. From 1807 to 1812, Russia temporarily cooperated with Napoleon against Sweden.
Napoleon wars (1805-1815)France and Russia signed a secret agreement. Trust the alliance which aimed to compel the Nordic countries to declare war against Great Britain. Russia attacked Poland and joined the coalition against Napoleon.
In July 1807, a new agreement was instead concluded in the secret Franco-Russian Treaty of Tilsit, which had significant consequences for Sweden. The treaty meant that the French Emperor and Tsar Alexander of Russia pledged not to wage war against each other but instead exert pressure on each other's enemies to surrender. Alexander I engaged in a war of words where they tried to shift the name of the Lyngenfjord mountain a few miles further west to claim a larger part of Norway and gain access to ice-free fjords such as Varanger, Tana, Laxe, Porsanger, and Altafjord, along with excellent harbors. They threatened Sweden with war. In the Convention of 1826, it was determined that the border between Norway and Russia would run along the Jakobs River.
The Finnish War of 1808-1809 was a conflict between Sweden and Russia The Finnish War of 1808-1809 was indeed a part of the larger Napoleonic Wars. Russian troops crossed the border into Finland on February 21st. France wanted Sweden to join the blockade against Britain, but the Swedes refused. As a result, Sweden was invaded by Russian forces from the north and east, primarily through Finland. Two battles took place in Sweden near Umeå in Ratan and Sävar. The conclusion of the Finnish War and the Treaty of Fredrikshamn in 1809 resulted in Sweden losing its eastern territories, which came under Russian sovereignty, including Finland, Åland, parts of Västerbotten, and areas that now belong to Russia. Norway, Denmark, and France fought on the side of Russia. From 1808 to 1809, Sweden was forced into conflict with Denmark in a war that neither side wanted. A few years later, in 1813, new hostilities arose, and the Danes were compelled to cede Norway to Sweden.
The wars during the reign of Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Here are some notable wars during this period: Russo-Turkish War of 1768-1774: This war was fought between Russia and the Ottoman Empire. Russia aimed to expand its influence in the Black Sea region and secure territorial gains. The conflict ended with the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca, which granted Russia territorial and trade concessions. War of the Bar Confederation (1768-1772): This conflict took place in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, involving a rebellion by the Bar Confederation against Russian influence. Russia intervened on behalf of the Polish king, resulting in the defeat of the confederation and the further weakening of Polish autonomy. Russo-Swedish War of 1788-1790: This war erupted between Russia and Sweden over territorial disputes in the Baltic region. Sweden sought to regain lost territories, while Russia aimed to consolidate its control over the region. The conflict ended with the Treaty of Värälä, which confirmed Russian gains in Finland.

1788 Swedish king Gustav III initiated a war against Russia due to the perceived threat of encirclement resulting from Russia's alliance with Denmark. In the second Battle of Svensksund in 1790, Russia suffered significant losses and lost half of its archipelago fleet.

1782 Swedes from Dagö, present-day Estonia, around 1,000 people, were resettled to Gammalsvenskby in southern Ukraine, which the Russians had conquered from the Turks. The forced relocation began in 1782, and nine months later they arrived. During the death march, more than half, especially children and the elderly, died. Many perished because they were unaccustomed to farming, having relied on fishing for their livelihood on Dagö. According to church records, only 135 individuals were still alive one year later.
The Cossack uprising of 1773-1774 The Cossack uprising, which ended with the rebel leader Pugachev being torn apart by four horses.
1768 Turkey declared war against Russia due to Russia's expansion in Poland. After the first war, the Russians conquered Crimea, which had been under the rule of the Ottoman Empire for nearly 300 years.
Catherine the Great made her lover Stanisław Poniatowski the king of Poland in 1764 and decided that Russia, Prussia, and Austria would annex parts of the country. She also attempted to persuade Finland to break away from Sweden and come under the protection of the Russian Empire.
The wars during the reign of Empress Elizabeth of Russia, 1741-1762.
When Elizabeth ascended to the throne, she revoked her promises of territorial concessions to the Swedes. Instead, she ordered her troops to invade Finland, which led to peace in Åbo (1743) where Russia annexed additional parts of the country.
The Northern Seven Years' War (1756-1763): This was a war between Russia and Sweden, which also involved other European countries. The war be after Russia attacked Sweden and other countries in the Baltic region.
The Wars of Russia (1741-1743): This was a war between Russia and Sweden, which also involved other European countries. The war be after Russia attacked Sweden and other countries in the Baltic region.
The Swedish diplomat Malcolm Sinclair was killed in 1739 by a Russian troop en route from the Ottoman Empire. The incident contributed to the Hats' failed war in Russia.

The Wars during the reign of Tsar Peter the Great (1682-1725):
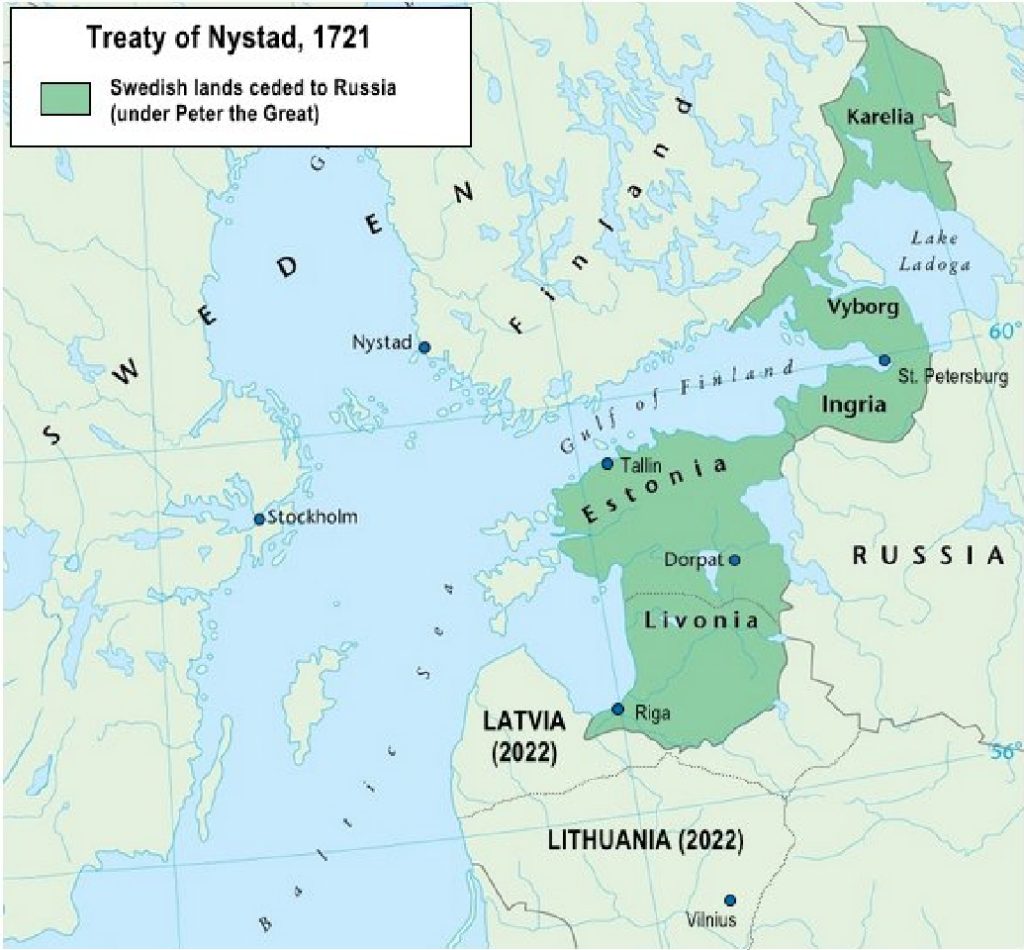
The Great Northern War (1700-1721)The Great Northern War, where Russia, Poland, Denmark, and Norway declared war against Sweden and launched a triple attack on the Baltic region. Peter the Great (reigned 1682-1725), who is a great idol of Putin, is criticized for his harsh treatment of political opponents and for using torture and murder to consolidate his power. Between 1719 and 1721, the Russians terrorized the Swedish coast and civilian population, which is referred to as the Russian pillaging.After the peace treaty in 1721, Russia acquired significant territories and gained direct access to the Baltic Sea through the Gulf of Finland.
Wars initiated by Russia in the 17th century and earlier.
The war between Russia and Sweden The war between Russia and Sweden (1655-1661), also known as Karl X Gustav's Russian War, was initiated by Russia. The causes of the war were partially territorial disputes over eastern Livonia and Russian efforts to increase their influence in the Baltic Sea region. The war began in 1655 when Russia attacked the Swedish territory of Ingria (now the Leningrad region). The Swedes responded by invading Karelia and Russia. After a series of victories for the Swedes, Russia regained the initiative and launched attacks on the Swedes in Finland, but their attempts to conquer Finland failed. In 1656, the war was brought to Poland, where Russia and Sweden fought for influence. The war between Russia and Sweden was one of the longest and bloodiest conflicts of the 17th century and had significant implications for the geopolitical development of the region. It also marked a significant shift in the balance of power between the countries, as Russia grew stronger while Sweden lost its colonies and territories in the Baltic Sea region.
Several of the Swedish wars, such as the The Gardie Campaign. The Gardie Campaign was about supporting Sweden's candidate for the Russian throne. In March 1610, the newly appointed Swedish Field Marshal Jacob De la Gardie marched into Moscow, which had been under siege by the Poles for two years. He was greeted with jubilation by the people as the savior and protector of the city.
The Crimean Khan Mengli Giray burned down Moscow in 1571. This khan also destroyed Kyiv in alliance with the Golden Horde. However, after the collapse of the Golden Horde, Moscow (the actual name of Russia) became his slaves, and their king became a vassal of the Crimean Khanate. Source
The Nordic Twenty-Five Years' War. The Nordic Twenty-Five Years' War (1570-1595) was initiated by Russia in Estonia and ended with a Swedish victory. The war was rooted in power struggles and territorial disputes between the countries in the Nordic and Eastern European regions.
The Livonian War of 1558: During the Livonian War, Ivan the Terrible initiated the Livonian War.ivonian war) During the Livonian War, Ivan the Terrible initiated a 24-year-long conflict (1558-1582) in an attempt to gain access to the Baltic Sea. He fought against various powers, including Sweden, Poland, and Lithuania. Ivan is notorious for committing numerous atrocities during his reign as Tsar, including murder, torture, and the displacement of populations. He is also responsible for a massive witch-hunt that resulted in several hundred deaths, as well as the killing of his own son. Under Ivan's rule, Russia launched large-scale exploration and colonization of Siberia. He granted the Stroganov trading family a charter to colonize extensive regions along major rivers such as the Ob and Irtysh.
Tönne Erikinpoika Tönne Erikinpoika led the Swedish delegation during the peace negotiations in Novgorod in 1510, where they decided to extend the ceasefire with Russia. He served as the commander of Viborg and Olofsborg between 1513 and 1520. When the Danish King Christian II defeated the supporters of Sten Sture in Sweden, Tönne Erikinpoika surrendered Viborg in November 1520.
The Russians entered Finland in 1495
According to Olaus Petri's chronicle.The Russians entered Finland and caused great damage. Knut Karlsson, who was the commander of Herr Sten's troops, was killed there, along with many others. They arrived in Viborg during the time of Saint Andrew and stormed the city. They entered a tower and occupied several places with ladders on the walls. When Knut Posse, who was in the city, saw this, he immediately set fire to the tower and burned them, causing the others who were on the walls to be frightened and flee.
Then they retreated to St. Olaf's Castle, where they also suffered great damage, and when they returned home, they had lost nine thousand people in the battles. After that, Mr. Sten arrived in Finland after the Russians had withdrawn. However, since the population was large and could not be kept together in one place for long, he dispersed them and allowed them to spread everywhere. But by the time of St. Catherine's Mass, the Russians returned, burning Karelia and Savonia, as well as a large part of Tavastia. They reached Häme Castle and burned everything, striking down anyone they could reach. And before Mr. Sten, who was then in Finland, could come to their rescue, the Russians had caused great devastation.
Holy Birgitta wanted to Christianize Russia
Magnus Eriksson initiates three wars against Russia: the Kexholm War of 1321-1323, the war against Novgorod in 1338-1339, and 1348-1351. In 1350, the Black Death strikes Sweden, leading to a drastic decrease in the population.
The Holy Crusades in Russia took place from 1348 to 1350 Saint Birgitta want Sweden to start a war and crusade against Russia to convert the Russian Orthodox. She hands over a manual on how the war should be conducted against God's enemies. King Magnus Eriksson buys into her reasoning and initiates the crusade as Birgitta desires. Sweden later loses the war against Russia due to the Black Death. Source
The Novgorodians' attack on Åbo (Turku) in 1318Åbo was a center for Finnish Christianity and a competitor to Novgorod.
Tyrgils Knutsson founded Viborg Castle in 1293
The Novgorodians' attack on Tavastia in 1292
Novgorod's attack. and Pskov's attack on Danish Estonia in 1268.
Tjuders, Karelians, and Russians raiding/plundering.
There are many Sámi stories about both enemies and friends, as well as how to interact with different groups, such as kvaner, Karelians, tethers and russiansThe Sámi legends and The Saga of Egil Skallagrimsson The Saga of Egil Skallagrimsson recounts conflicts with the Tjuder, Karelians, and Russians and likely has had a real historical background. The Tjuder were said to have lived in the area east of Estonia and south of Lake Ladoga. In Sámi legends, the Tjuder are described as active and aggressive. According to these Sámi legends, the Tjuder raided storages, burned down tents, and killed people.
Often, the greatest enemies come from distant regions that are difficult to define, and they engage in plundering, which suggests that the Kvens were not enemies of the Sámi. As the Grand Prince of Novgorod emerges during the 11th and 12th centuries, he has Karelian and Tjuder vassals who seek plunder. Their interests do not lie in maintaining good relations; instead, they rely on a plunder-based economy where they hold power and influence.
The fictional Battle of Neva became the starting point for Russian propaganda.
The alleged Battle of Neva is a central part of Russian propaganda and historical revisionism. According to the Russian narrative, Swedes, along with Norwegians, Finns, and Tavastians, led a large army to attack Novgorod in 1240. This account is described in the Novgorod Chronicle, which was written much later, in the 14th century.
The Neva River flows from Lake Ladoga into the Gulf of Finland, where present-day St. Petersburg is located. The Battle of Neva gained more details during the 17th century and attained almost biblical proportions. Aleksandr Nevsky has become Russia's national saint, and there are many streets and places named after him.
There are several historical objections to this battle, primarily the fact that it is not mentioned in any Swedish medieval sources. Additionally, no Swedish bishops died during this time. Subsequent research has questioned the significance of the battle and viewed it as a regular border conflict that has been exaggerated for political purposes. This also explains why it is not mentioned in Swedish or other Western sources.
Erik the Holy was king from 1234 to 1250 and was succeeded by Valdemar Birgersson from 1250 to 1275. Valdemar, born in 1239, was the son of Birger Jarl, who is likely the prince referred to in the Novgorod Chronicle. Birger Jarl founded Stockholm in 1252. The first known Swedish military expedition against Novgorod after the events at Neva took place in 1256. one hypothese. the claim that the battle revolves around Bishop Thomas leading the Swedish soldiers is disputed.
Russian attacks on Tavastland, Finland and Estonia
Yaroslav's Grand Duke of Novgorod's attack on Tavastland 1227-1228
Yaroslav, the Grand Prince of Novgorod attacks on Estonia, Yem, and Karelia. 1222, 1226-1227
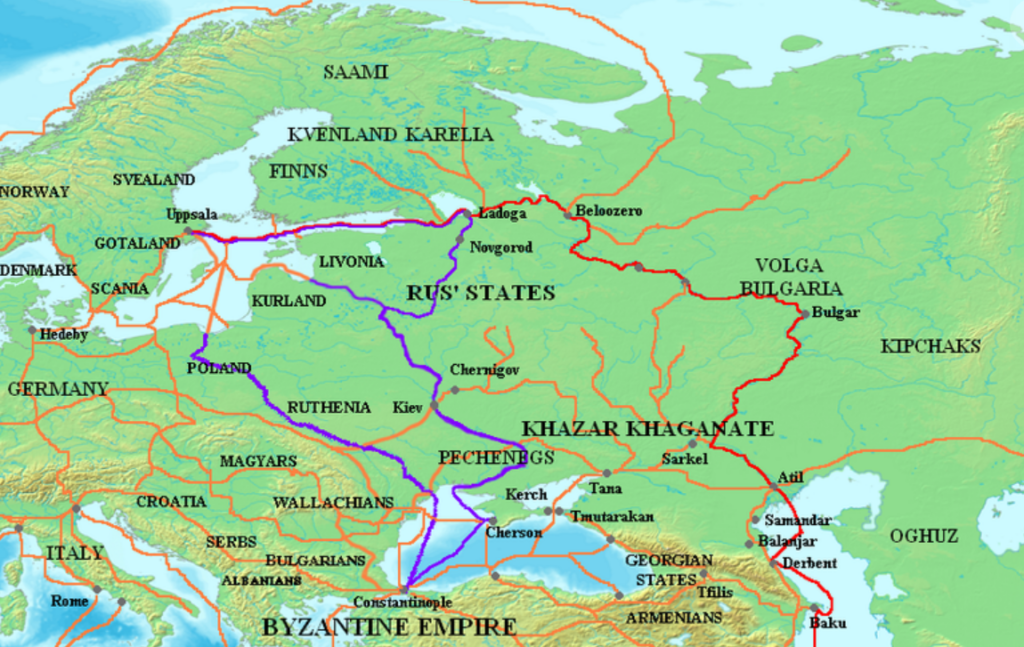
Russia and its first rulers are said to have descended from Swedish Vikings
Putin, who is interested in history, uses his propaganda speeches to claim that Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia share the same spiritual Orthodox roots. He aims to create a Russian identity, asserting that it is one nation and one people. Russian nationalist historians, like Boris Rybakov aligning with the political will and supporting this through anti-normanism which is a movement of historical revisionism that focuses on the origins of Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus, emphasizing the Slavic development. Within this framework, there is a political desire to downplay the real and historical influences from Scandinavia.
A Nordic name is Valdemar, which is a variation of the Russian name Vladimir, meaning "ruler of the world." It was Emperor Vladimir I who chose to Christianize the realm in the 10th century and earned the epithet "the Holy." Vladimir had spent some time in exile in the Kingdom of Svea before returning in 980 to seize power in Gardariki, which encompassed much of present-day European Russia. The Kievan Rus' adopted Christianity in 988 from Constantinople rather than Rome.
The numerous Scandinavian archaeological finds and runestones suggest connections to the Swedish Vikings, strongly indicating extensive trade and the likelihood that the Rus' people had their origins in Sweden. Rurik, ca 830,to 879 was according to Kyiv Nestor chronicle Swedish Vikings from the tribe of the Rus (identified with the Svear).[1] ) who is said to be the founder of Kingdom of Kiev and progenitor of it royal family who ruled Russia until 1598. The word Rus which is also found in the word Roslagen refers to rowers is the origin of the name Russia. Source




